The Science Behind Scent: How Aromatherapy Actually Works in Your Brain
Take a moment to think about your most vivid scent memory. Maybe it's your grandmother's kitchen during holiday baking, the ocean breeze from a perfect vacation, or that specific perfume that instantly transports you back to your college years. Within milliseconds of catching that familiar aroma, you're not just smelling—you're remembering, feeling, and sometimes even healing.
This isn't poetry or wishful thinking. It's neuroscience.
While skeptics dismiss aromatherapy as "just nice smells," researchers have been quietly mapping exactly what happens in your brain when therapeutic-grade essential oil molecules meet your olfactory system. The results reveal a sophisticated biological process that explains why certain scents can measurably reduce stress hormones, improve sleep quality, and even influence immune function.
For women over 40 who are serious about evidence-based wellness, understanding this science transforms aromatherapy from alternative therapy to informed self-care strategy.
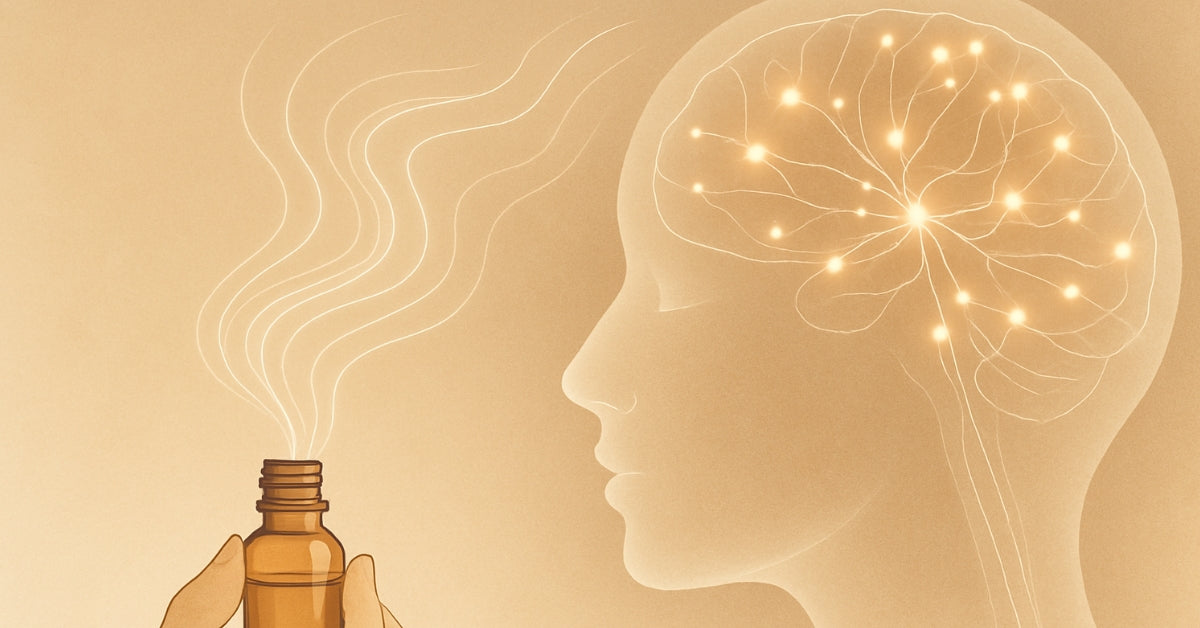
The 0.2 Second Journey: From Nose to Brain
The Most Direct Route to Your Brain
Unlike every other sense in your body, smell has a direct highway to your brain's emotional and memory centers. When you inhale lavender, bergamot, or frankincense, you're not just experiencing a pleasant fragrance—you're triggering a complex neurochemical cascade that affects your entire body.
Here's what happens in those crucial first moments:
Step 1: Molecular Recognition (0.0-0.1 seconds) Essential oil molecules dissolve into the mucus lining of your nasal cavity, where millions of olfactory receptor cells are waiting. Each receptor is specialized to recognize specific molecular shapes—like a lock waiting for the right key.
Step 2: Neural Translation (0.1-0.15 seconds) When the right molecule meets its receptor, an electrical signal fires directly to your olfactory bulb, which sits just behind your nose and is actually part of your brain, not your peripheral nervous system.
Step 3: Limbic System Activation (0.15-0.2 seconds) This signal travels instantly to your limbic system—the ancient brain network that controls emotions, memories, hormones, and survival responses. No other sense has this direct access.
Why This Direct Route Matters for Wellness
This bypassing of your conscious thinking brain is precisely why aromatherapy can feel so immediate and sometimes surprising in its effects. You're not deciding to feel calmer when you smell lavender—your limbic system is already initiating the calm response before your conscious mind fully processes the scent.
The Three Brain Regions That Make Aromatherapy Work
The Hippocampus: Your Memory and Learning Center
What It Does: The hippocampus processes and stores memories, particularly emotional memories. It's why certain scents can instantly transport you to specific moments in your past with startling clarity.
How Essential Oils Interact: Research shows that specific essential oil compounds can enhance hippocampal function, potentially improving memory formation and recall. This is particularly relevant for women over 40 who may be noticing subtle changes in memory or concentration.
The Science Behind Memory Enhancement: Studies on rosemary essential oil demonstrate measurable improvements in memory performance through hippocampal stimulation. Participants who worked in rosemary-scented environments showed improved recall and task accuracy compared to unscented control groups.
Practical Application: Using frankincense or rosemary while learning new information or during mentally challenging tasks may enhance cognitive performance and memory formation.
The Amygdala: Your Emotional Processing Center
What It Does: Your amygdala is your brain's alarm system, constantly scanning for threats and triggering emotional responses. It's also where anxiety, fear, and stress responses originate.
The Aromatherapy Connection: Certain essential oil molecules can measurably calm amygdala activity, reducing the intensity of stress responses and anxiety reactions. This isn't just feeling better—it's actual changes in brain activity visible on neuroimaging scans.
Evidence from Neuroimaging Studies: Brain scans of people inhaling lavender essential oil show decreased amygdala reactivity to stress-inducing stimuli. The calming effect isn't placebo—it's measurable changes in neural activity.
Why This Matters for Women Over 40: As life stressors compound—career pressure, family responsibilities, health concerns—your amygdala can become hyperactive. Aromatherapy provides a tool for directly modulating this hyperactivity at the neurological level.
The Hypothalamus: Your Hormone Command Center
The Master Controller: Your hypothalamus regulates hormone production, body temperature, sleep cycles, appetite, and stress responses. It's the bridge between your nervous system and endocrine system.
How Scent Influences Hormones: Essential oil molecules can trigger hypothalamic responses that affect cortisol production, melatonin release, and even reproductive hormones. This explains why aromatherapy can have such profound effects on sleep, stress, and hormonal balance.
The Clary Sage Example: Clary sage contains sclareol, a compound that can influence estrogen receptors through hypothalamic pathways. This isn't folk medicine—it's documented hormonal modulation through olfactory-hypothalamic connections.
The Neurochemistry of Specific Essential Oils
Lavender: The GABA Connection
The Mechanism: Linalool and linalyl acetate, lavender's primary compounds, increase GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) activity in your brain. GABA is your primary inhibitory neurotransmitter—it literally slows down neural activity and promotes calm.
Measurable Effects:
-
Decreased cortisol production within 30 minutes of inhalation
-
Increased parasympathetic nervous system activity
-
Enhanced slow-wave sleep patterns
-
Reduced anxiety markers in both blood tests and brain scans
Why Quality Matters: Synthetic linalool doesn't produce the same neurochemical responses as naturally derived compounds. The complex molecular profile of therapeutic-grade lavender creates effects that isolated compounds cannot replicate.
Bergamot: The Cortisol Regulator
The Active Compounds: Limonene and linalyl acetate in bergamot have been shown to reduce cortisol production and modulate stress response systems.
Clinical Evidence: Studies measuring salivary cortisol before and after bergamot inhalation show significant reductions in stress hormone levels. Participants also reported improved mood and reduced anxiety.
The Unique Benefit: Unlike lavender, which primarily promotes calm, bergamot appears to specifically target chronic stress patterns while maintaining alertness and mood elevation.
Frankincense: The Neuroinflammation Fighter
Beyond Aromatherapy: Frankincense contains boswellic acids that can cross the blood-brain barrier and reduce neuroinflammation—a factor in cognitive decline and mood disorders.
The Dual Action: Through inhalation, frankincense affects the limbic system for immediate emotional benefits. Through topical absorption, it provides longer-term neuroinflammatory benefits.
Research Findings: Studies show frankincense can enhance learning, reduce anxiety, and improve immune function through both olfactory and systemic pathways.
The Nervous System Response: Parasympathetic Activation
Understanding Your Two Operating Systems
Sympathetic Nervous System (Fight or Flight):
-
Increased heart rate and blood pressure
-
Elevated stress hormones
-
Heightened alertness
-
Decreased digestion and immune function
Parasympathetic Nervous System (Rest and Digest):
-
Slower heart rate and breathing
-
Reduced stress hormones
-
Enhanced digestion and immune function
-
Optimal conditions for healing and restoration
How Aromatherapy Shifts the Balance
The Vagus Nerve Connection: Certain essential oils can stimulate vagal tone—the strength of your vagus nerve, which controls parasympathetic responses. Higher vagal tone correlates with better stress resilience, improved mood, and enhanced immune function.
Measurable Changes: Heart rate variability studies show that specific essential oils can shift your nervous system into parasympathetic dominance within minutes of inhalation.
The Quality Factor: Why Molecular Integrity Matters
Synthetic vs. Natural: The Neurochemical Difference
The Complexity Advantage: Natural essential oils contain hundreds of molecular compounds that work synergistically. Synthetic versions typically contain only the primary active compound, missing the supporting molecules that enhance effectiveness.
Research Evidence: Brain imaging studies comparing natural vs. synthetic lavender show different patterns of neural activation. Natural lavender produces broader, more sustained limbic system responses.
The Entourage Effect: Like cannabis compounds working together for enhanced effects, essential oil molecules appear to work synergistically for optimal neurochemical impact.
Adulteration and Neurological Response
The Hidden Problem: Many commercial essential oils are diluted with carrier oils, synthetic compounds, or cheaper plant materials. These adulterants can actually interfere with the intended neurological responses.
Detection Through Response: If an essential oil doesn't produce the expected calming, energizing, or mood-lifting effects, adulteration may be interfering with proper receptor binding and neurochemical cascades.
Dosage and Timing: Optimizing Neurological Impact
The Goldilocks Principle
Too Little: Insufficient molecular concentration may not trigger adequate receptor activation for measurable neurological effects.
Too Much: Overwhelming olfactory receptors can cause adaptation, where your nose stops responding to the stimulus, reducing effectiveness.
Just Right: 2-3 drops in a diffuser for 15-30 minutes provides optimal concentration for sustained neurological benefit without receptor fatigue.
Timing for Maximum Effectiveness
Circadian Considerations: Your olfactory sensitivity and neurochemical responsiveness vary throughout the day. Evening aromatherapy tends to produce stronger parasympathetic responses, while morning use may enhance cognitive benefits.
Hormonal Timing: For women experiencing hormonal fluctuations, aromatherapy effectiveness may vary with your cycle. Tracking responses can help identify optimal timing for specific oils.
Building Your Science-Based Aromatherapy Practice
Start with Measurable Outcomes
Rather than hoping for vague "relaxation," identify specific, measurable goals:
-
Sleep quality (track sleep duration and wake frequency)
-
Stress levels (monitor physical tension and emotional reactivity)
-
Cognitive function (notice memory, focus, and mental clarity)
-
Mood stability (observe emotional balance throughout the day)
The 21-Day Neural Pathway Protocol
Week 1: Baseline and Single Oil Focus Choose one oil for one specific outcome. Use consistently at the same time daily. Notice subtle changes in your target area.
Week 2: Refinement and Timing Adjust dosage and timing based on your body's responses. Your nervous system is adapting and may require different approaches.
Week 3: Integration and Combination Add a second complementary oil or create simple blends. Your neural pathways are now familiar with the primary oil and ready for more complex combinations.
Quality Assessment Through Body Response
Immediate Indicators (Within 5 minutes):
-
Noticeable shift in breathing depth
-
Subtle changes in muscle tension
-
Mood or energy level changes
Short-term Indicators (Within 30 minutes):
-
Changes in mental clarity or focus
-
Shift in emotional state
-
Physical sensations of calm or energy
Long-term Indicators (After consistent use):
-
Improved sleep patterns
-
Better stress resilience
-
Enhanced mood stability
-
Increased overall well-being
The Future of Aromatherapy Science
Emerging Research Areas
Personalized Aromatherapy: Scientists are exploring how individual genetic variations in olfactory receptors might predict which essential oils work best for each person.
Precision Timing: Research into chronobiology and aromatherapy is revealing optimal timing for different oils based on circadian rhythms and individual sleep-wake patterns.
Combination Therapies: Studies are examining how aromatherapy enhances other wellness interventions, from meditation to hormone therapy.
What This Means for You
As research continues to validate and refine our understanding of aromatherapy's neurological mechanisms, the practice becomes less about belief and more about informed application of scientifically-supported interventions.
You're not just buying into alternative therapy—you're utilizing evidence-based tools for neurological and hormonal optimization.
Making Informed Choices
Questions to Ask Your Essential Oil Provider
About Neurological Effectiveness:
-
Can you provide third-party analysis of active compounds?
-
How do you ensure molecular integrity during processing?
-
What extraction methods preserve the full compound profile?
About Quality Assurance:
-
Are your oils tested for adulteration?
-
Can you provide batch-specific chemical analysis?
-
How do you verify therapeutic potency?
Red Flags for Neurological Effectiveness
Marketing Claims Without Science: Be wary of companies making specific medical claims without citing peer-reviewed research.
Impossibly Low Prices: Oils that produce genuine neurological effects require high-quality sourcing and processing, which has associated costs.
Lack of Safety Information: Companies serious about neurological effects provide detailed safety guidelines and contraindication information.
Your Next Steps in Science-Based Aromatherapy
Start Simple: Choose one oil with well-documented neurological effects (lavender for stress, bergamot for mood, or frankincense for cognitive support).
Track Responses: Keep a simple log of your physical, emotional, and cognitive responses to establish your personal response patterns.
Quality First: Invest in certified organic, therapeutically tested oils from companies that provide transparency about their sourcing and testing.
Build Gradually: Allow your nervous system to adapt and respond before adding complexity to your aromatherapy practice.
The science behind aromatherapy reveals it to be far more than pleasant scents—it's a sophisticated method of directly influencing your brain chemistry, hormone production, and nervous system function. When you understand the mechanisms, you can use aromatherapy not just hopefully, but strategically.
Your brain is already equipped with the pathways to benefit from therapeutic aromatherapy. The question isn't whether it works—it's whether you're ready to use it intelligently.
Discover essential oils backed by science and third-party testing, formulated to work with your brain's natural pathways for optimal wellness outcomes. Quality matters when you're targeting specific neurological responses.